With additive manufacturing experiencing significant growth in recent years, the EDF Pulse Ventures team explored the opportunities offered by metal additive manufacturing. In collaboration with several Group entities, the corporate venture defined 3 major advantages for EDF of using this technique, and identified innovative start-ups in the field.
Traditional metal fabrication methods, such as casting, forging and machining, are well established and widely used. For certain applications, however, they present limitations, notably in terms of raw material consumption, manufacturing lead times, design flexibility and environmental impact. Additive manufacturing offers potential solutions to these problems, particularly in specialized industries such as energy, aerospace, marine and medicine. However, high costs have historically limited its widespread use. Recent advances should reduce these costs and enhance process quality, enabling additive manufacturing to expand into these sectors.
What is metal additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing is the process of producing metal parts using 3D model data and layer-by-layer assembly. There are different categories of process, adapted to different use cases:
| Process | How it works | Use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Powder bed melting | A thin layer of metal powder is spread, then selectively fused by laser or electron beam | Complex, detailed parts |
| Directed energy deposit | The metal, in powder or wire form, is melted directly by a laser or electron beam at the point of deposition | Repair parts, add features to existing parts, manufacture large parts |
| Material projection | Droplets of metallic material are selectively deposited and then solidified | Precision parts, metal prototypes, small production runs |
| Binder spraying | A liquid binder is selectively deposited on a bed of metal powder. The part is then sintered in a furnace | Rapid prototyping, large parts, medium production runs |
| Material extrusion | A filament containing metal particles is extruded. The part is then sintered to remove the binder | Prototyping, non-structural parts, education |
According to various reports1, the metal additive manufacturing market recorded annual growth of 23% between 2016 and 2022. This trend is set to continue, with a forecast annual growth rate of 24.4% in 2024, which is expected to continue through to 2030. As a result, the global metal additive manufacturing market is expected to grow from $3.5 billion in 2023 to around $20 billion in 2030. A set of indicators that prompted EDF Pulse Ventures to take a closer look at the subject.
[1] AM Power and Wholers
EDF Pulse Ventures identifies 3 major advantages for EDF in using metal additive manufacturing
The EDF Group, like many industrial companies, needs numerous custom metal parts to operate its facilities, particularly for its industrial activities in nuclear, hydraulic and thermal power. In collaboration with these Group businesses, EDF Pulse Ventures has identified three main advantages to using metal additive manufacturing for certain EDF Group uses.
-
Efficiency and quality
Metal additive manufacturing offers the possibility of producing parts with complex geometries, impossible to achieve with traditional methods such as machining or forging. This technology also speeds up the prototyping process, enabling faster time-to-market. What's more, some metal additive manufacturing techniques enable higher-quality finished products.
-

Economy
Unlike subtractive methods, additive manufacturing uses only the necessary amount of material, which significantly reduces waste. Additive manufacturing also enables on-demand production, reducing the need for large inventories and the associated storage costs.
-

Environmental impact
Traditional metal manufacturing's dependence on fossil fuels results in high CO2 emissions. By producing parts on demand, additive manufacturing reduces the need for large inventories and, consequently, the logistical footprint and energy consumption associated with storage and transport.
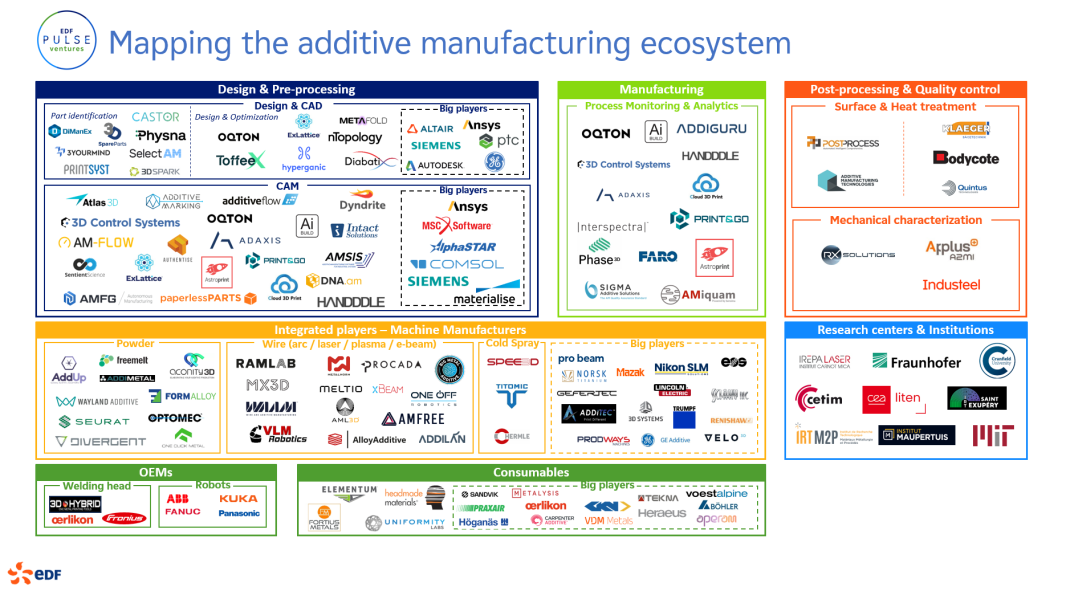
EDF Pulse Ventures identifies innovative start-ups in the metal additive manufacturing ecosystem
As part of this study, EDF Pulse Ventures identified around a hundred players, including numerous start-ups specializing in metal additive manufacturing. These innovative companies can help the Group to position itself effectively in this field.